How Is the Vsepr Theory Used to Classify Molecules
The Lewis structure gives you the number of bonding electron pairs and lone pairs that surround a molecules central atom. The molecular structure is given by the VSEPR Theory.
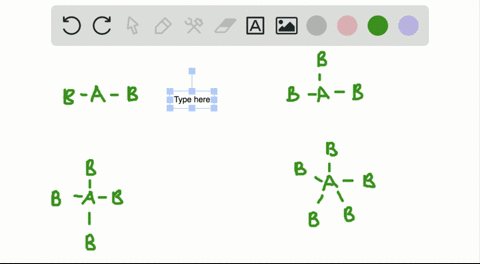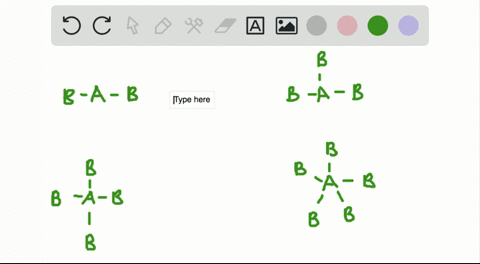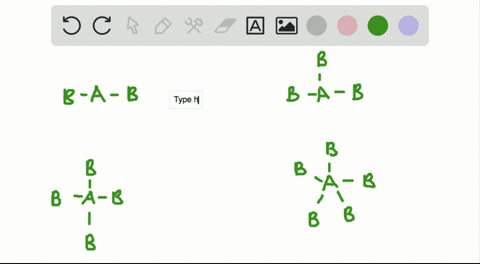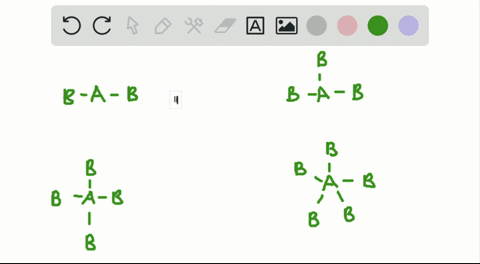
Solved A How Is The Vsepr Theory Used To Classify Molecules B What Molecular Geometry Would Be Expected For Mathrm F 2 And Mathrm Hf
This is done by examining the electron pairs surrounding the central atom.

. The Lewis structure of CO 2 Figure 1 shows only two electron groups around the central carbon atom. The valence shell electron pair repulsion VSEPR model predicts the shape of individual molecules based on the extent of electron-pair electrostatic repulsion. With two bonding groups and no lone pairs of electrons on the central atom the bonds are as far apart as.
As organic chemistry is a 3D-based science the shapes of molecules are extremely important for the complete understanding of organic reactions and properties of molecules. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is a method of predicting the geometry of molecules. The VSEPR theory assumes that each.
Predicting the Shapes of Molecules. According to VSEPR the valence electron pairs surrounding an atom mutually repel each other. You should have a good comprehension on this topic.
The average distance between two bonded atoms. VSEPR theory Valence Shell Electron Pair Repusion is what we use to explain the shapes of molecules in Chemistry. Valence shell electron pair repulsion VSEPR theory ˈ v ɛ s p ər v ə ˈ s ɛ p ər VESP-ər.
410 və-SEP-ər is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. The VSEPR theory is used to predict the shape of the molecules from the electron pairs that surround the central atoms of the molecule. It is based on the core concept that electrons repel one another due to their similar charges and molecules construct themselves in a way that puts the greatest possible distance between lone electron pairs.
It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm. Conclusion It can be concluded that the Lewis electron-pair theory cannot be used to find out the structure of molecules and the number of lone pairs in a molecule whereas the VSEPR model is beneficial. Determines the shape of the molecules based on the number of bonded electrons and lone pairs around central atom.
Because you will hardly meet relevant to this when you study organic and inorganic chemistry too. VSEPR is a topic in general chemistry. How is the VSEPR theory used to classify molecules.
VSEPR and Geometry of Organic Molecules For smaller molecules we have a central atom based on which we determine the molecular geometry. The shapes of these molecules can be predicted from their Lewis structures however with a model developed about 30 years ago known as the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR theory. The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion VSEPR Theory is used to predict the 3-dimensional shape of covalent molecules.
It uses the lewis dot structures to predict the shapegeometry of a molecule. The valence shell holds the electrons that are involved in bonding and are the electrons shown in a Lewis structure. I think my following explanation wi.
The theory was first presented by Sidgwick and Powell in 1940. The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory VSEPR states that Whenever there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms the atoms will arrange themselves in a geometric shape so as to minimize the electron pair repulsion. The vsepr theory valance shell electron pair repulsion is used to determine the shape of the electron domains and the shape of the molecule itself.
VSEPR is used together with Lewis structures to determine the shapes of molecules. VSEPR theory classifies molecules geometrically according to the approximate arrangement of sigma bonds and lone pairs around their central atom. The model states that electron pairs will repel each other such that the shape of the molecule will adjust so that the valence electron-pairs stay as far apart from each other as possible.
So arrange a good basement and mighty foundation on this topic. We can talk about the VSEPR as a starter all the way up to enzymes and everything in between when we are discussing shapes of molecules. The VSEPR model can be used to find out the structures of molecules having no central atoms which is much more complex in comparison to the structures mentioned above.
For example let us predict the structure of a gaseous CO 2 molecule. I have said before that Size Matters in Chemistry but shape also matters. The VSEPR theory helps us to predict the 3D shapes of the molecules.
How is the VSEPR theory used to classify molecules. For more details see the first two answers below and Dennis Sardellas answer to How do we determine the bond angles for molecular geometries that have lone pairs around them eg bent trigonal pyramidal seesaw etc. The VSEPR theory was developed in 1945 by Russian physicists Victor Kekule and Alexander Müller who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1970.
However when working with larger organic molecules it may not be accurate to say that this molecule is tetrahedral or trigonal planar etc. The repulsion between valence electron pairs on the central atom determines the shape of the molecule. These configurations are called altitude and meridian.
In an ionic crystal ions minimize their potential energy by combining in an orderly arrangment. The acronym VSEPR stands for the valence-shell electron pair repulsion model. VSEPR theory can be used to predict the structure of molecules.
It is a fact that electron pairs arranged around a. They adopt an arrangement that minimizes this repulsion thus determining the molecular geometry. Application of VSEPR Theory.
It states that certain inorganic molecules have stable configurations with alternating single and double bonds which can be used to explain their spectral lines. The VSEPR theory is based on the assumption that the molecule will take a shape such that electronic repulsion in the valence shell of that atom is minimized. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory vesper for short classifies molecules on the basis of the number of electron pairs bonding and lone pairs associated with the central atom.
What molecular geometry would be expected for F2 and HF. From knowing the shape of the molecule you. There is no direct relationship between the formula of a compound and the shape of its molecules.
The concept of hybridization helps us understand the bonding in organic molecules.
How Does The Vsepr Theory Classify Molecules Quora
How Does The Vsepr Theory Classify Molecules Quora
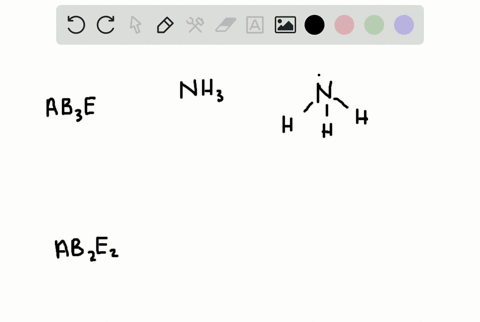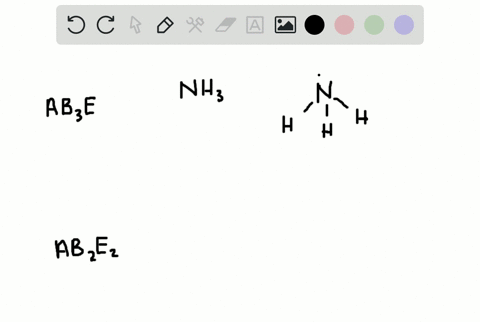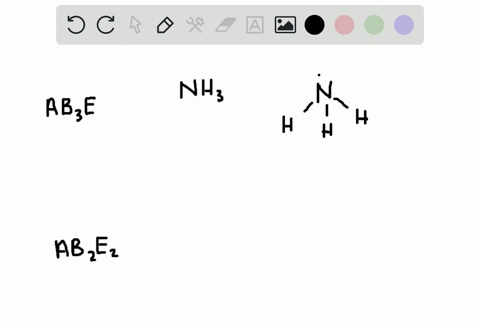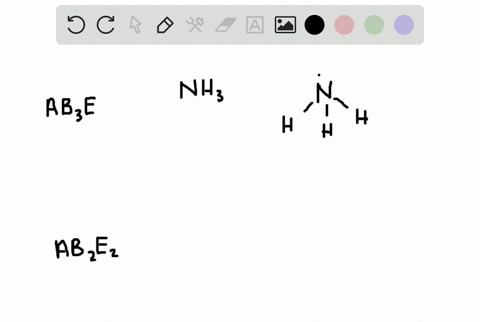
Solved A How Is The Vsepr Theory Used To Classify Molecules B What Molecular Geometry Would Be Expected For Mathrm F 2 And Mathrm Hf
No comments for "How Is the Vsepr Theory Used to Classify Molecules"
Post a Comment